How Does Bread Get Black Mold?

Have you ever left a loaf of bread on the counter, only to find it covered with dark, fuzzy spots a few days later? That’s black moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More at work – a particularly unsettling and unwelcoming guest who thrives in our kitchens’ forgotten corners.
With its sinister appearance, black moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More can turn a fresh product into something inedible. Bread can grow moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More relatively quickly, making it essential to consume the food within five to seven days. Here’s a look at how bread develops black mold.
What is Mold?
Similar to mushrooms, moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More is a type of fungus that thrives both indoors and outdoors. Although moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More resemble tiny plants, they are neither plant nor animal. Rather, moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More is a living organism that feeds off of decaying matter, such as rotting wood, or even food, such as bread. When these sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More land on a damp surface, they can grow and form colonies, which are often visible as fuzzy or slimy patches in a variety of colors such as green, black, white, or blue.
MoldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More are nourished by three food sources: moisture, organic matter, and oxygenOxygen is a chemical element essential for combustion and li... More. Damp areas are notorious for harboring moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More colonies since they provide a constant supply of moisture that steadily feeds the sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More. Organic matter provides a food source for moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More, creating a consistent food source. While some molds play a beneficial role in nature by breaking down dead organic matter, others can spoil food, damage property, and pose health risks.
How Does Black Mold Grow on Bread?
Bread molds are known to colonize different types of breads. The sugar and carbohydrates contained within loaves of bread offer ample supplies of nutrients to the sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More. These rich organic materialsOrganic materials are derived from living organisms, such as... More can spur moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth within a short span of five to seven days.
The species of moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More that develops on the bread depends on the type of sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More that linger in the immediate environment. Rhizopus stolonifera, also known as black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More, is one common moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More that affects bread. This type of moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More grows everywhere on the planet.

Moist conditions are ideal for the growth of black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More. Due to this reason, black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More will grow on wild fruits and vegetables, too. As the moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More consumes the organic material, it causes rotting. Black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More is known to even kill plants.
As it starts to grow on the surface of bread, black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More appears as velvety blue or green patches. When the bread is left untouched for days, these unsightly blue and green patches develop centers that are noticeably black and splotchy—hence its name, black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More. The moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More may or may not develop a musty smell as well.
How Quickly Does Black Mold Grow on Bread?
Exposure to moisture and air can trigger black bread mold growth. Organic white bread does not contain preservatives, which means black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More will grow on these loaves the fastest. When left at room temperature and exposed to moisture, white bread can develop moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More in five days.
The speed at which black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More grows on loaves also depends on the acidity of the bread and its moisture contentMoisture content is the amount of water present in a materia... More. Most breads are non-acidic and contain a pH level of seven. Sourdough bread has a higher acidic level in comparison to white bread, so moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More develops more slowly.
Bread may seem dry, but it contains a large amount of moisture. Moisture from the inside of baked bread travels to the outside. The crust may become noticeably softer, for instance. When storing bread in a plastic bag, moisture will be evident; and moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth can occur.
Furthermore, the temperature at which the bread is stored plays a large part in how fast a loaf will develop black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More. Leaving a loaf of bread exposed to moisture and air will invite a flurry of mold spores, especially considering that moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More thrives in humid environments.
A room temperature of 86 to 98 degrees Fahrenheit can spur certain types of moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth. However, storing bread in the freezer at 32 degrees Fahrenheit will stop the chances of moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growing on the loaf. Freezing bread prevents moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth altogether.
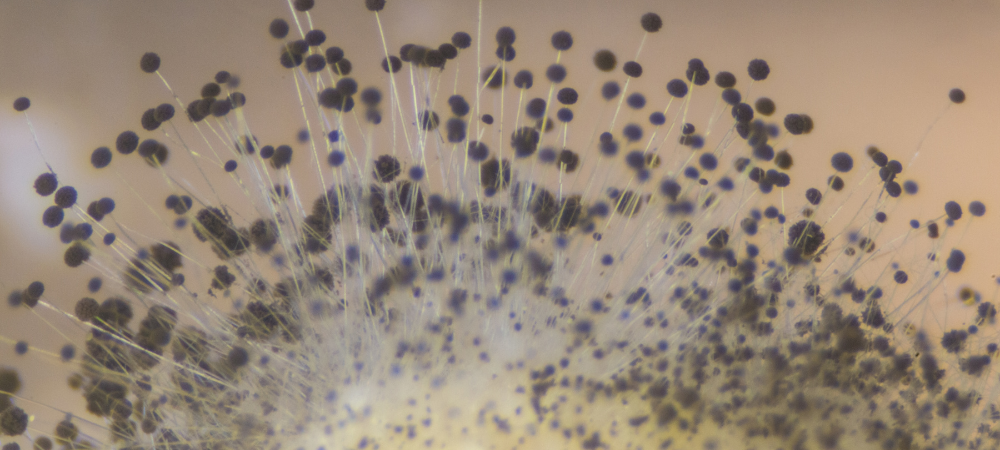
Is Eating Bread With Black Mold Harmful?
Taking a small bite out of a moldy slice of bread is generally not harmful. However, severe reactions can develop in individuals who are allergic to moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More. Upon inhaling the sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More, the moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More can trigger respiratory issues, especially in people suffering from asthma or immune diseases.
Consuming larger amounts of bread contaminated with black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More can cause severe illness. An individual who ingests a large amount of moldy bread can experience an upset stomach and be exposed to mycotoxinsMycotoxins are toxic substances produced by certain types of... More. MycotoxinsMycotoxins are toxic substances produced by certain types of... More are harmful when inhaled or eaten, potentially causing fatigue and rashes.
When noticing black bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More, it is wise to discard the entire loaf. Mold spores are microscopic and difficult to detect until they grow into larger clusters. MoldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More can also grow deep roots without detection; so, avoiding sickness to varying degrees is best done by throwing out the moldy bread.
Bread moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More can also generate unpleasant odors when left in a trashcan inside the house, read How to Remove Odors from the Trash Can for proper solutions to remove the odors.
How is Black Mold Prevented on Bread?
As previously mentioned, freezing bread prevents moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth. Additionally, consume the bread within two to three days—before moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More has a chance to grow. Avoid slicing the bread, which accelerates the rate of spoilage. Also, store the bread in a dry bread box or paper bag to reduce moisture buildup.
MoldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More colonies are notorious for spreading rapidly, which is why it is important for homeowners to immediately address a moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More problem. You must call a professional who provides quality mold removal services to residential homes and commercial properties.
Professional moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More cleanup technicians use high-tech equipment to locate all moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth within the property. Upon finding both hidden and visible moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth, they contain the areas to prevent contaminationContamination is the presence of harmful or unwanted substan... More to other parts of the building. Using advanced methods, specialists eliminate all moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More growth.
Structural materials may be permanently damaged by the moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More colonies. MoldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More removal technicians also provide restorationRestoration is the process of returning a property to its pr... More services to affected areas and remove components that are beyond repairRepair is the act of fixing or restoring damaged property, m... More. A key part of mold remediationMold remediation is the process of identifying, removing, an... More is to fix the moisture source that triggered the moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More invasion.

Delays in stopping a moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More invasion can leadLead is a heavy metal that can be toxic to humans, especiall... More to structural damage to building components. MoldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More sporesSpores are microscopic reproductive units of fungi or mold t... More eat away at organic materialsOrganic materials are derived from living organisms, such as... More, including drywall, causing the weakening of building materials. Health problems, from itchy skin to watery eyes, can also develop in the building’s occupants.
When you need help to remove a moldMold is a type of fungus that grows in damp or humid conditi... More problem, call a professional for skilled mold cleanup techs to ensure your building is mold-free.












